
Central Sleep ApneaĪlso called CSA, Central Sleep Apnea 10 is when the brain doesn’t send the proper signals to the muscles that control breathing, resulting in repetitive periods of breathing disturbances while sleeping. CaffeineĬaffeine is a commonly used mild stimulant that is most often found in coffee, sodas, teas, dark chocolate, certain supplements, and energy drinks.
It includes episodes of voluntary muscle weakness followed by intense emotion. CataplexyĬataplexy 9 is one of the physical features of the sleep disorder narcolepsy. It is thought to be useful in helping people focus, though more research needs to be done on this. Where white noise contains all the frequencies of sound blended equally, brown noise puts more energy on the lower frequencies, creating a more bass type of sound. Brown Noiseīrown noise 8 is a low-frequency noise that can help listeners feel relaxed.
While this light can be beneficial during the day, as it boosts attention, alertness, and mood, it can have a negative impact on sleep when viewed at night. Like the other colors on the spectrum, blue light is naturally emitted by the sun but more often, when we refer to blue light we are talking about the blue light from screen devices like cell phones and computers. Blue Lightīlue light 7 is one of the colors of light on the electromagnetic spectrum. This was a practice much more common in medieval times 6 and these days is more often caused by a sleep disorder. Rather than sleeping once throughout the night, a biphasic sleeper might sleep for four hours at night and four more during the day. Biphasic Sleepīiphasic sleep is sleep that is divided into two sessions per day. It is often prescribed for people with sleep apnea, COPD, or other conditions that affect breathing during sleep. This machine helps push air into the lungs via a mask and nasal plugs that are connected to the ventilator. Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BPAP) DeviceĪ BPAP is a type of ventilator – a device that helps with breathing. This is also normal and can occur about two or three times per night. When you become aware of an awakening, it becomes an observable wake-up. Usually, mini-awakenings go completely unnoticed and can occur up to 20 times per hour. AwakeningsĪwakenings 5 are the moments we wake up throughout our sleep at night. It is typically diagnosed in childhood and often lasts into adulthood. Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)ĪDHD 4 is a common neurodevelopmental disorder, in which symptoms include difficulty paying attention, inability to control impulsive behaviors, or over-activity. Conversely, some sleep disorders are caused by the lack of atonia during REM sleep, which can lead to excessive muscle twitching or movement. During REM sleep, it is normal to experience atonia. AtoniaĪtonia 3 means loss of muscle definition. In terms of sleep, artificial light can have an impact on your circadian rhythm. Artificial LightĪrtificial light includes any source of light produced by electricity or artificial means. For example, acute sleep deprivation 2 usually lasts for a matter of days, whereas chronic sleep deprivation is longer-term. When we use the word “acute” in terms of sleep, we’re talking about a condition or state that is not permanent but rather short-lived.
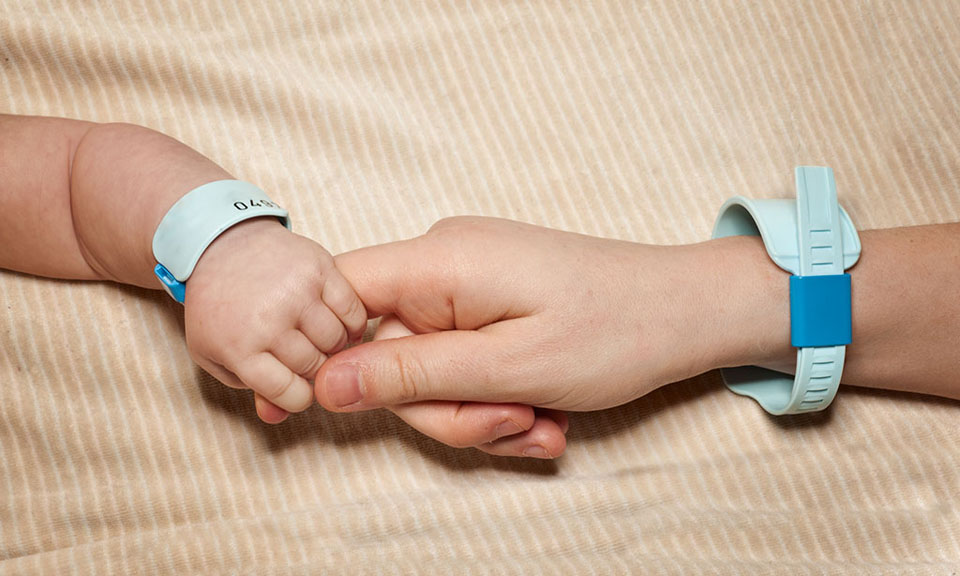

It’s usually measured by wearing an actigraph, a small wristband-like device, which measures sleep cycles and can help diagnose certain sleep disorders. Actigraphy 1 is a technique used to measure cycles of activity and rest over several days or weeks.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
